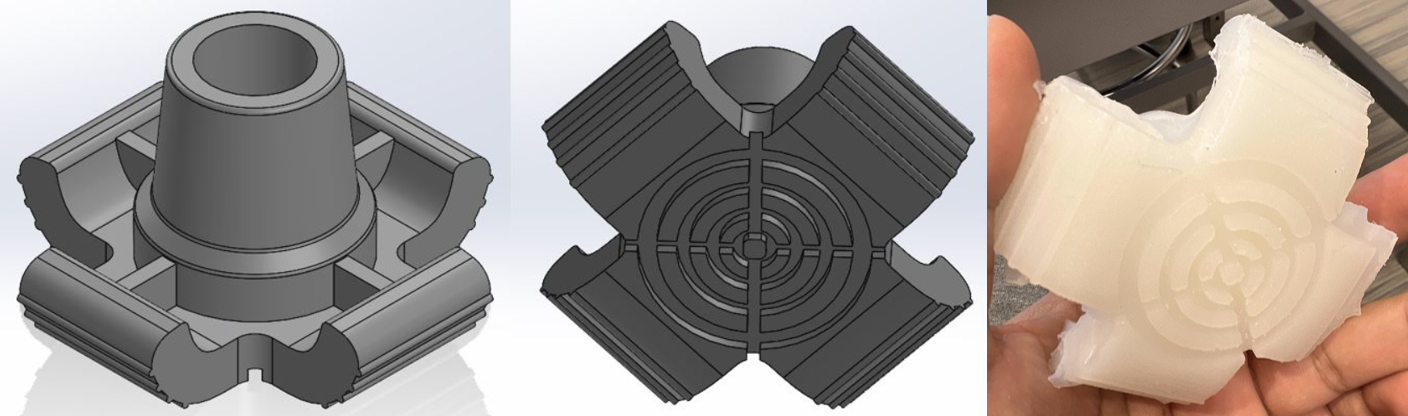
Base Geometry
The anti-slip design features four fins added to the existing axillary crutch base geometry, which serve to increase the surface area and points of contact made with the ground during ambulation. Each fin includes four ridges for additional traction during the swinging phase of ambulation. Current axillary crutch bases have a circular face at the bottom of the base, so the surface area of contact between the base and the ground is limited to the leading edge of the circular face during the swinging phase of ambulation. However, this design adds an additional 1.67 in2 of surface area on each fin to allow for a greater surface area of contact during the swinging phase of ambulation and reduce slipping potential.
Irrigation System
The anti-slip design also features four circular cuts on the underside of the base component for added traction, with four straight-line cuts beginning at each corner and ending at the center of the base. These cuts serve as irrigation channels for any fluid trapped underneath the base, allowing the fluid to to drain and further reduce the slip potential.
Decision Matrix 1 – Base Design
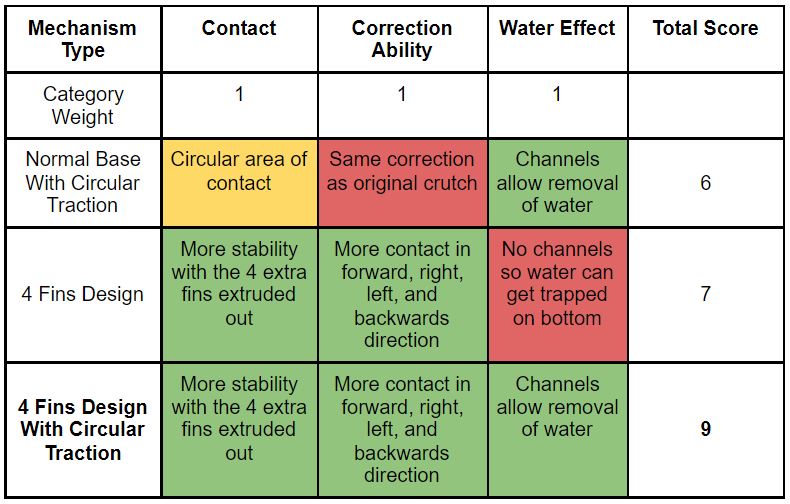
Weighting system:
Green = 3
Yellow = 2
Red = 1
Decision Matrix 2 – Base Material
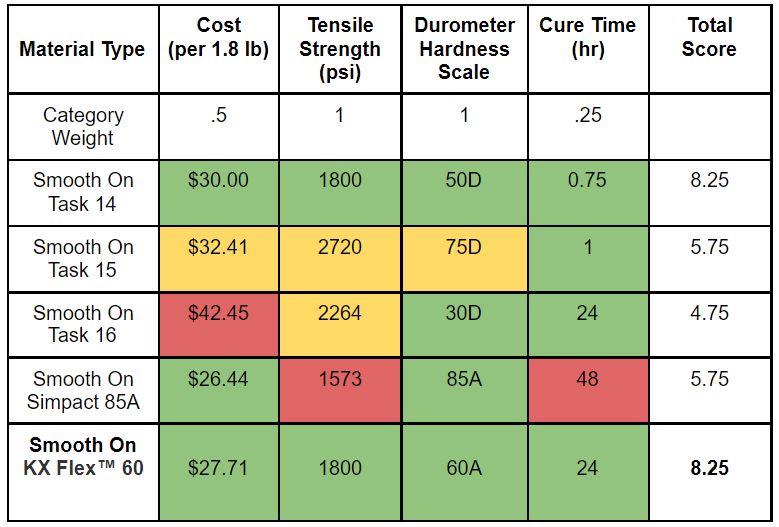
Weighting system:
Green = 3
Yellow = 2
Red = 1