The Vertical Agriculture Device has come far from its initial design days. After numerous iterations and presentations, the current prototype is comprised of three subsystems:
- Irrigation System
- Rotating Rack
- Growbed
The system is enclosed in a 5’ x 4’ x 4’ T-slot frame, plywood, and glass. This is to ensure a sturdy structure to ensure protection of the plants from pests and the outside environment. It also allows for a more controlled atmosphere to promote plant growth. It’s split between two sections, the plant housing unit and the component unit. The housing space is where the grow beds will be placed on the rotating racks and hold the plants. The component unit is where the motor, the water pump, and electrical components are located.
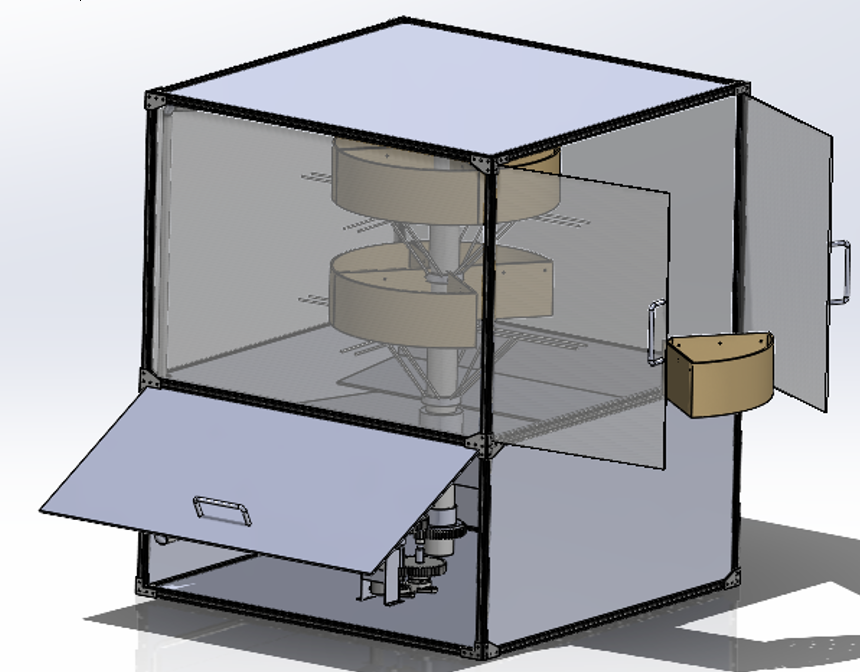
Figure 1: The current assembly with all the components.
The Irrigation system
The goal of the irrigation system is to cycle water into a sprinkler and water the plant in a periodic interval. The current pump that is being used cycles one gallon of water per minute into the system. The water then travels through the grow beds and into the water retrieval reservoir. This allows for the water to gather in a specific location and protect the components in the component space.
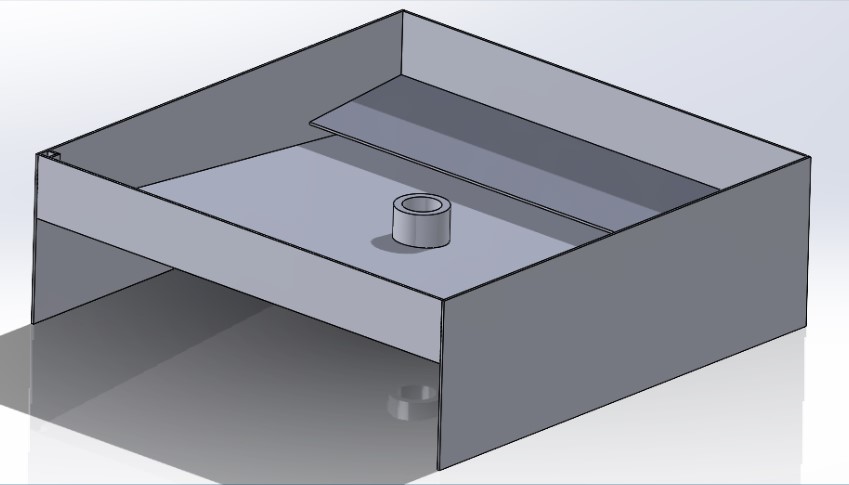
Figure 2: Water Retrieval System
Rotating Rack
The rotating rack offers the opportunity for the grow bed to get access to sunlight as the day progresses, allows the sprinkler to spray nutrient water on the plants, and allows the user to easily retrieve the grow beds opposite of the user. It operates from a motor that outputs 21 rpm. This is then translated between 1:5 gear ratios to lower the gears to 0.84 RPM.
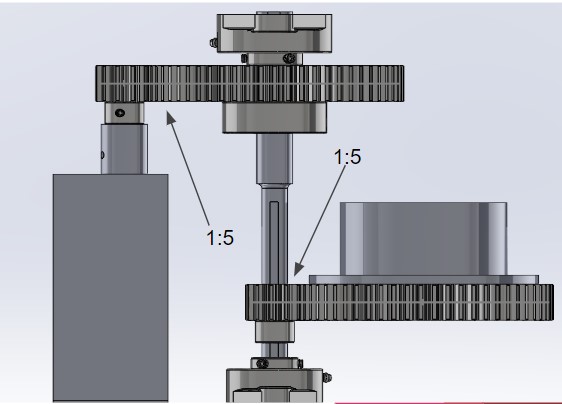
Figure 3: Current Gear Ratio
Grow Bed
The grow bed offers a space for the plants to grow within the system. It is designed and going to be manufactured in 3D printed ABS plastic to offer a food-safe and easily manufactured component. One grow rack will support 4 grow beds. They have holes in the bottom of the grow bed that allow for water to trickle out of the bed and into the system. It also has baffles in order to prevent water from spilling out of the system.
Figure 4: Quarter GrowBed
What is Next?
The next process is to begin the construction of the frame and the growth of our testing plant, tomatoes, in order to have them in a state where they can be placed into the grow beds.
