Design Solutions
Design Solution: Material Selection for Interface
Main goal: model characteristics similar to that of a human’s nasal cavity and nasopharynx at the interface (where NGT contacts device)
- Mold will be utilized to create the interface
- Identified need for resin
- Researched materials known for their biofidelity in terms of human tissue

Characteristics of focus: Young’s modulus,viscosity, texture, ease of casting and tactile feedback to the user
Decision Matrix: Material Selection
| Price | Ease of casting | Young’s Modulus | |
| Vinyl Terminated Polydimethylsiloxane resin (1,000 cSt) | $26/100g | Double casting | 0.36 – 0.87 MPa |
| Ecoflex™ 00-30 | $6/100g | Vacuum degassing | 0.1 MPa |
| Dragon Skin™ 10 NV | $4/100g | No VD or double casting | 1 MPa |
Design Solution: Sensor Incorporation
Option 1: Extruding Sensors
Main idea: Placing sensors directly along the pathway through which NGT travels
Advantage: Accurate pressure readings
Disadvantage: Inaccurate representation of insertion training process
- Creates unwanted friction that will alter user’s technique
Option 2: Integrating sensors in divots
Main idea: Form divots in inner framework large enough to encapsulate the sensors
Advantage: Favors fluidity and realism of insertion process
Disadvantage: Less accurate pressure readings
- Would need to establish acceptable buffer & pressure value thresholds
Decision Matrix : Sensor Selection
| Cost | Sensing Range | Size | |
| Interlink FSR UX 400 Short | $3.99 | 0.5 N to 150 N | 7.2 mm diameter |
| FlexiForce A301 Sensor | $56.96 total, $14.24 per sensor | 0 to 445 N | 14 mm diameter |
| Interlink FSR UX 406 Short | $4.99 | 0.5 N to 150 N | 34 mm2 area, square 5.8 mm per side |
| Interlink FSR 402 | $7.00 | 0 to 100 N | 14.7 mm diameter |
Design Solution: Support Structure
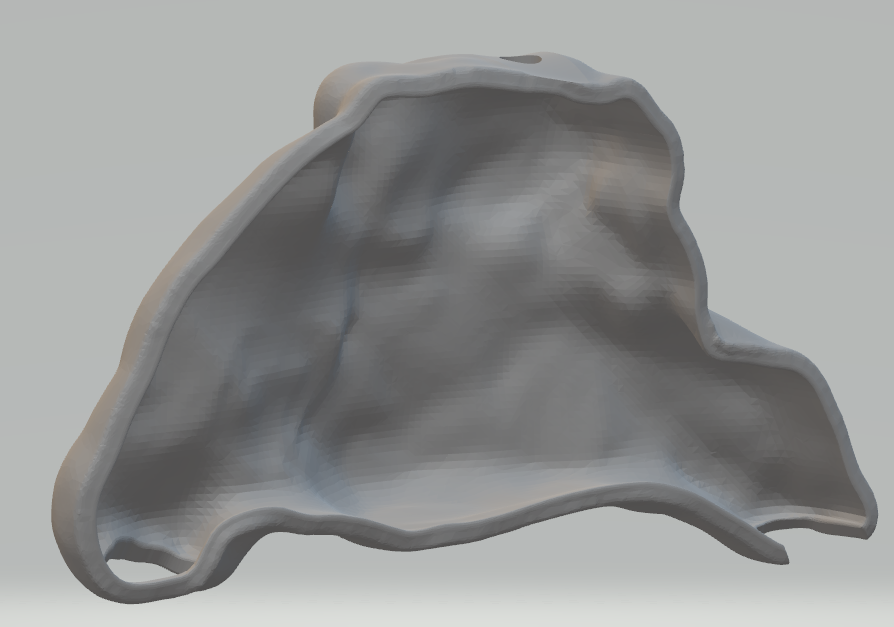
- Main goal: be able to support the sensors and the model of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx
- Physiological model based on: CT scans obtained from Dr. Anthony Lau
- modeled using Mimics Innovation Suite
- Support structure for the anatomical model will be a block component
Design Solution: Notification System
Option 1: Light By Part
Main idea: Wiring multiple sensors into one light, one light per anatomical section
Advantage: Fewer lights for the user to keep track of
Disadvantage: Feedback is less precise, hard to differentiate exact location
Option 2: Light By Location
Main idea: Wiring each sensor to its own light
Advantage: Will be better able to determine where force is in excess
Disadvantage: Too many lights may confuse user as to which sensor is experiencing pressure
Decision Matrix
| Clock Rate | Price | Dimensions (mm) | Programming Language | Power Draw (mA) | |
| Arduino Mega 2560 Rev3 | 16 MHz | $18.40 | 101.5×53.3 | C++ | 20 |
| Raspberry Pi Zero W | 1 GHz | $10.00 | 66.0 x 30.5 | C/C++/Python | 80 |
| Teensy 4.0 | 600 MHz | $19.95 | 35.6 x 17.8 | C++ | 100 |